Can the inverters AC connect to conduits directly?
The solar cable, as the name suggests, acts as a channel where electricity travels. As an indispensable part of the solar energy system, it is also vital to understand and learn it.
Solar Cables in a Photovoltaic System
In our lives, where there is electricity, there are wires and cables, and photovoltaic systems are no exception. A solar system consists of one or more solar panels as well as inverters and other hardware. In order to make full use of sunlight, the photovoltaic system or solar panel, needs to be well connected and assembled to work properly. The photovoltaic cable plays a crucial role in connection process.
What Are they?
Solar cables are designed to transfer DC current in a photovoltaic system. They are used as cables to connect solar panels and photovoltaic arrays in a solar system.
- They have high mechanical strength and can withstand relatively harsh weather conditions. In solar projects, solar cables are mostly laid outdoors and exposed to high temperature.
- They are likely to face harsh conditions during their long-life span of about 20 to 25 years. Therefore, it is important to equip your solar system with high quality solar wires and cables.
- The classification of solar cables is based on the number and specifications of the wires. In addition, the diameter also depends on the number of wires and specifications.
The classification of the solar Cable
The photovoltaic power generation system can be divided into DC cable and AC cable. The DC cables between the photovoltaic panels, and the DC cables between the parallel photovoltaic panels, occupies more than half of the cable amount. After traveling through the inverters AC, cables are used to transfer the electricity to the power grid.
According to the different application environment, the cable of photovoltaic power generation system can be divided into:
- DC cable
(1) For cables between photovoltaic panels arrays, photovoltaic certificated cables should be used.
(2) Parallel cables run between photovoltaic panels arrays and between photovoltaic panels arrays and the DC distribution box.
(3) Cables between DC distribution box and inverter.
- AC Cable
- Connecting cables between inverter and booster transformer.
- Connecting cables between booster transformer and distribution device.
- Connecting cables between the distribution device and the power grid or users.
Here we focus on the selection and laying of AC cables in grid-connected photovoltaic power generation.
In a photovoltaic system, the temperature of AC cables varies due to different installation environments. The distance between the inverter and the grid connecting point is not the same, resulting in different voltage drops on the cable. Temperature and voltage drop will affect the loss of the system, so it is necessary to design the AC cable diameter to the inverter properly. Taking all factors into consideration such as the initial investment of photovoltaic power plant being reduced, and the wire loss of the system should be cut.
- The output current of the inverter and the cable carrying capacity should be consistent
Inverter output current is determined by power, single-phase inverter rated AC current = power /230, three-phase inverter rated AC current = power /230/3, and some inverters can also be 1.1 times overload on ac output.
Cable current carrying capacity is determined by the material, wire diameter, and temperature. Cable can be divided into 2 two kinds; copper wire and aluminum wire. Each has its advantages. If the ambient temperature is higher than 35℃, the allowable current should be reduced by about 10% when the temperature increases by 5℃. If the ambient temperature is lower than 35 ° C, the allowable current will increase by about 10% every time the temperature decreases by 5 ° C. Generally, if the cable is installed indoors in a ventilated place, the maximum ambient temperature is below 40 ° C. If the cable is installed outdoors in a sunny place, the maximum ambient temperature may reach 50 °C.
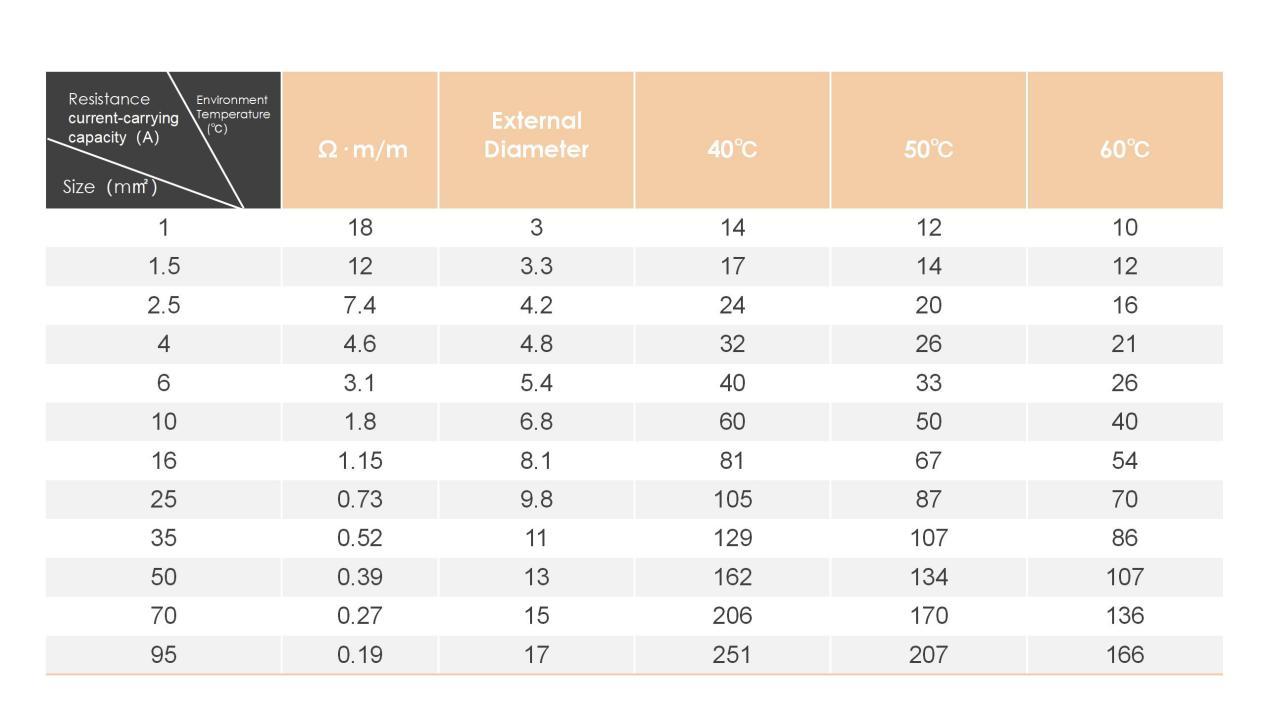
- Economy of cable selection and design.
In some places, the inverter is far away from the point of grid connection. Although the cable can meet the requirements of the load, the cable wire is longer. This will cause the wire a relatively larger loss. You can consider using a cable with larger diameter to reduce the loss, because the larger the cable, the less internal resistance. Meanwhile the price of the cable, and whether the inverter AC output has been connected to the conduit directly should also be considered.
Whether the inverter AC output cable can be connected to the conduit involves a very important step in the installation process of the inverter.
Connect cables to the AC output side
AS/NZS1429.1:2006 stipulates that cables must be put into the conduit outdoors and can be exposed in places inaccessible to people indoors. DC cables must be put into conduit fully and the length of exposed cables next to the inverter should not exceed 30cm.
Although the photovoltaic cables in a solar project can withstand UV radiation, extreme temperature and humidity, and are durable, we still need to put the AC cables into the solar conduit for safety and beauty.
If a solar installer ever tries to install a PV system on your house without using conduit to protect the wiring, you can call the power company and ask them if conduit installation is necessary in PV systems? If they say yes (which they will), fire him immediately before he burns down your house.
What is conduit?
Before you learn how to install a conduit, let’s learn what a conduit is.
Conduit is a hard, durable protective tubing that completely covers and protects wires or cables used in electrical applications that typically need protection from exposure to sunlight and other elements.
When installing conduit, wire is pulled through the conduit tubing and then typically passed through walls, fixed to the exterior of the house, or to the interior of a house to connected the sub meter box. Basically, conduit installation protects the wires running through your walls, underground, on your roof, or down the side of your house.
Types of Conduit
Some of the more popular types of conduit that are used in electrical work include rigid-steel, electrical metallic tubing (EMT), rigid non-metallic (poly vinyl chloride – PVC), and flexible metallic and nonmetallic conduit.
Installation of conduit
Installing the conduit involves measuring the length of the conduit, cutting, threading, bending it to fit the requirements of your project, installing fittings and brackets, fixing the conduit in the right place, installing the connector, threading the conductor (wire) through the conduit, and making the fixing and testing connections.
When installing, make it run as straight as possible to avoid any unnecessary bending.
。
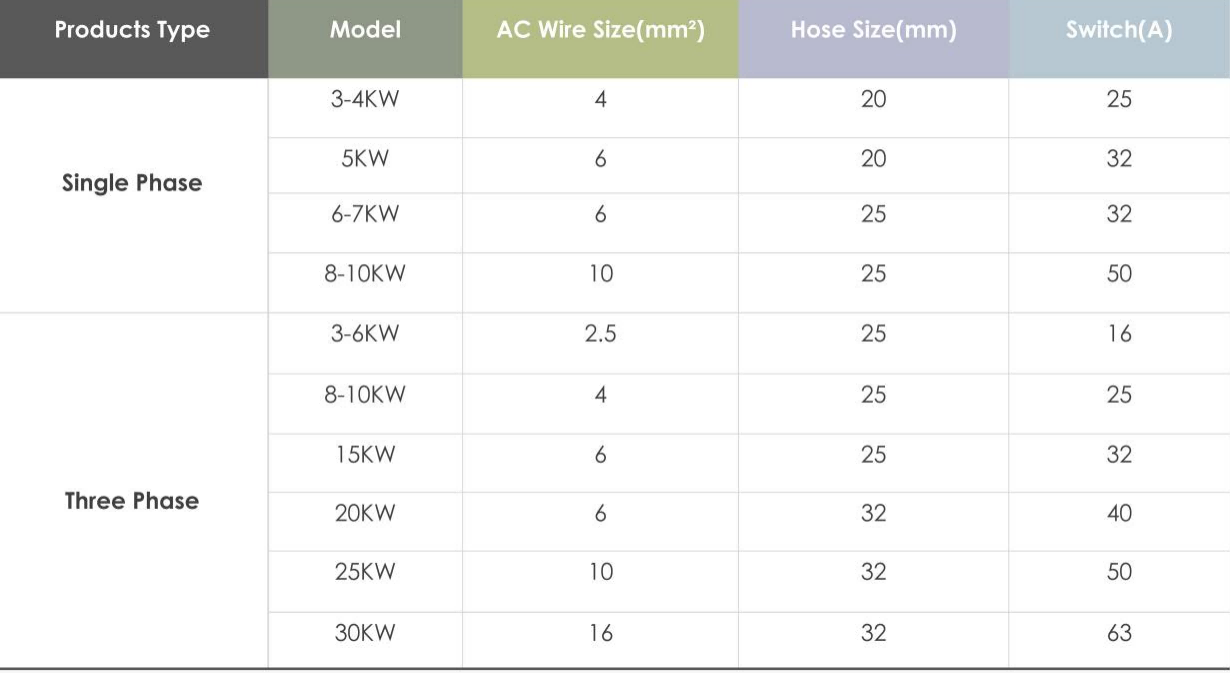
Quite a few brands do not take the conduit installation into account when designing the AC output side, resulting in the need to add extra glans and connectors during installation, which is a waste of time and labor cost. And when there are parts of the AC wire are exposed, it looks extremely ugly. Some brands do this part perfectly, such as Solar edge and Each Energy. Each Energy, in particular, has made sufficient consideration in the design of AC output side. All models ≤10kw’s AC wires can be directly plugged into the AC conduit with 20 mm diameter. Each Energy also gives different reference values for different models, with appropriate conduit sizes and AC switch size.
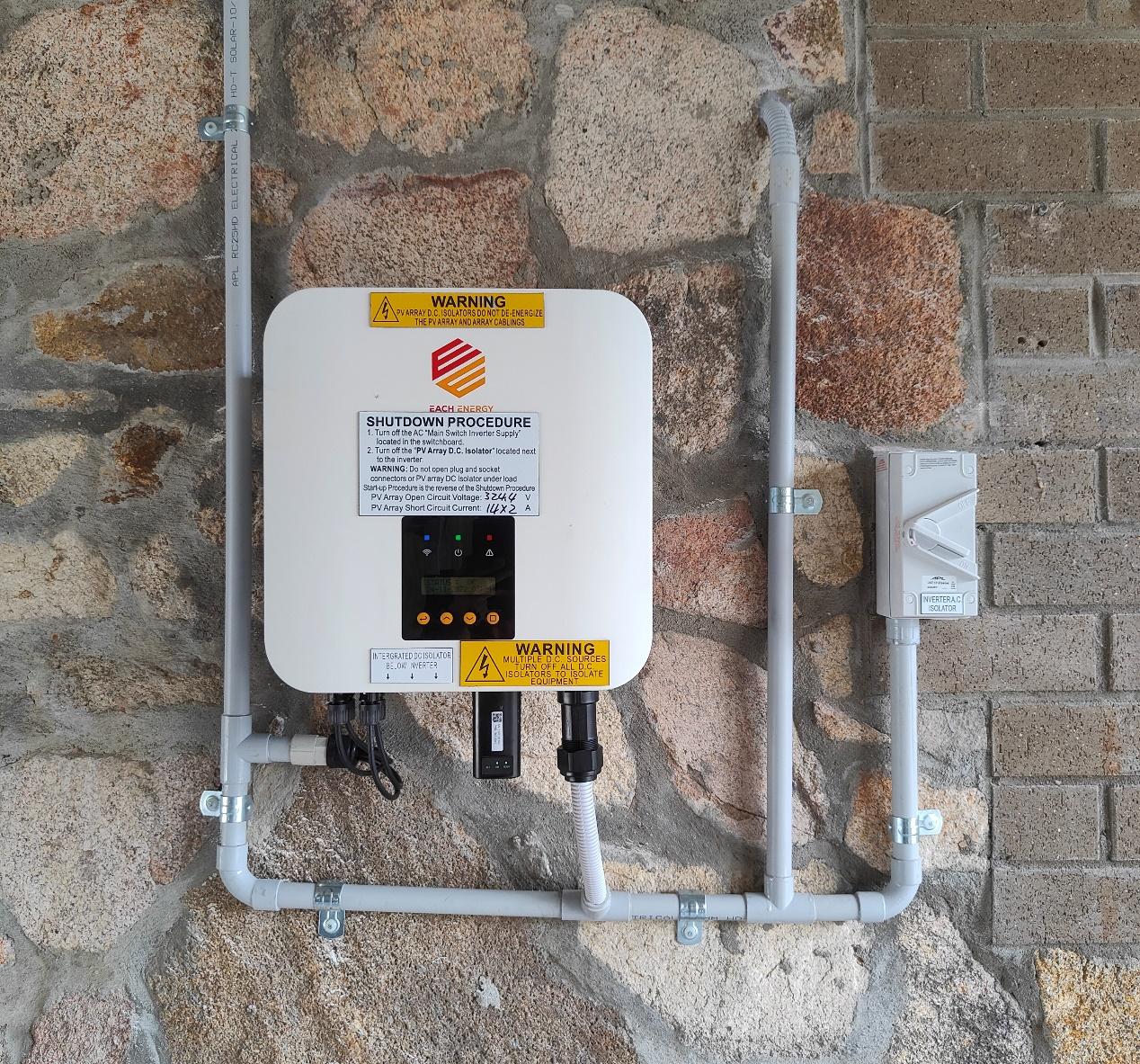

In a solar system without conduit, outdoor wires can be exposed to the sun, get wet and eventually corrode. Your PV system may suffer extensive and costly damage.
Also, without a conduit, the wires in the wall could heat up and start a fire. Installing conduit is vital to protect your wires from all external or internal elements and vice versa.
